What is Pharyngitis?
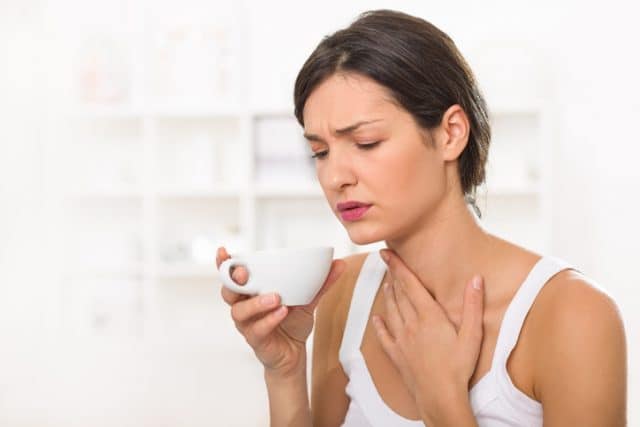
Pharyngitis is the technical term for one of the most common forms of a sore throat, which is caused by a temporary inflammation of the pharynx. The pharynx is the membrane-lined cavity located behind the mouth and nose. It connects both of these to the esophagus. It is one of the most common reasons for doctor visits and is more likely in the colder months of the year.
Causes of Pharyngitis
Swelling in the rear portion of the throat behind the tonsils and larynx is the characteristic cause of pharyngitis symptoms. This most usually arises from a viral infection. The common cold and flu are the most frequent culprits. However, a wide range of viruses may also be responsible.
In addition to viruses like mononucleosis and chickenpox, pharyngitis can be caused by bacterial invasion by streptococcus (Strep A), whooping cough, and diphtheria. During a diagnosis, your doctor will rule out these more serious potential causes.
Symptoms of Pharyngitis
Symptoms typically include sore throat, fever, headache, and joint or muscle aches. Some less common symptoms of pharyngitis include skin rashes and swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
When pharyngitis appears with cold or flu, it can have additional symptoms. Cough and sneezing with a low fever may indicate a cold, while a fever above 102°F may indicate the flu.
Diagnosis of Pharyngitis
There are three tools that can help with the diagnosis of pharyngitis:
Physical Examination-Diagnosing pharyngitis begins by looking at the patient’s throat using a simple light. Presence of the illness can be indicated by white or gray patches, swelling, or redness. The doctor will also feel the neck for the signs of swollen lymph nodes.
Throat Culture-A throat culture is employed when the doctor suspects pharyngitis is caused by strep throat. A cotton swab is used to obtain a sample of secretions from the throat. A rapid in-office test provides some preliminary evidence; if it comes back positive, a further analysis takes about 24 hours.
Blood Tests-Blood work is ordered when unusual causes of pharyngitis may be in play. A small blood sample will be drawn from the patient’s hand or arm. A complete blood count (CBC) is used to discover underlying infections. Blood testing is the fastest way to verify the presence of mononucleosis.
Treatment of Pharyngitis
No medication can directly eliminate the viruses responsible for most cases of pharyngitis. If a viral infection is the cause, the patient may be prescribed medication to help with pain and make the symptoms more bearable. Within 2-3 weeks, most cold and flu infections subside naturally.
Home remedies may include things like drinking plenty of water to fend off dehydration, eating warm broth or chicken soup, gargling with salt water, or using a humidifier. No matter what the cause may be, it’s important to get as much rest as possible.
If you believe you are experiencing symptoms of pharyngitis, make an appointment with New York ENT. Our board-certified physicians have extensive experience diagnosing and treating a wide variety of ear, nose, and throat conditions.